
THE ROAD TO HEALTH SERIES: Light and Sleep. S. Kilichowski
Sleep problems are a real blight on our lives. Sebastian Kilichowski discusses the influence of light on sleep quality and suggests what to do to sleep better in this post from the series “The Road to Health. Do you know that…?” ?
What does sleep have to do with light? It turns out that actually quite a lot and we’re about to find out what it is.
Hardly anyone realizes that we spend on average 1/3 of our lives sleeping! Sleep is responsible e.g. for how we feel, how much energy we have and what the composition of our body looks like!
It’s a good idea to visualize sleep as a time to rest and repair after a busy day. If we do a lot of brain-work, practise sports professionally, or even train for ourselves, we should care about proper regeneration of our brain and body at night as much as possible so that we wake up refreshed and ready to start a new day.
What Happens When We Don’t Sleep Well?
Here are some little-known facts:
1) 1 sleepless night is enough to reduce the number of NK by 72% (Natural Killers), that is, specialized cells of the immune system whose main task is to fight viruses and infections.
2) People who regularly sleep fewer than 7 hours have a higher BMI and are more likely to be obese than people who sleep more. This has to do with the influence of sleep on the levels of hunger and satiety hormones, inflammation, as well as a reduction in insulin sensitivity, which can lead to weight gain in people who eat large amounts of carbohydrates.
3) Poor sleep and not getting enough sleep can mess with our hormones, especially in the level of estrogen and progesterone, which makes us more irritable and prone to mood swings and quarrels, especially in relationships with a partner.
Sleeping Difficulties
If you suffer from these 7 symptoms, you have trouble sleeping:
- you find it hard to fall asleep;
- you feel sleep-deprived in the morning;
- you have cravings for sweet or salty snacks in the second half of the day;
- you wake up at night and need to visit the toilet between 2am and 3am;
- it’s hard for you to get up in the morning;
- you need coffee to actually wake up;
- you set 5-10 snoozes in your alarm clock before you finally get up.
Light and Sleep
Ok, you already know that sleep is very important and it’s nice to make it as high-quality as possible. You must be asking yourself now, what is the relationship between light and sleep?
In this article, we will discuss one very important factor that has a huge impact on our sleep, energy levels, and how we feel. This factor is greatly underestimated and few people take it into account. It is… light! Before we find out what all the fuss is about, let’s first read a bit about the circadian rhythm.
Circadian Rhythm
Research studies into the circadian rhythm and its influence on our body have been carried out for many years and have been appreciated in 2017 when the scientists involved in those projects were awarded Nobel Prize in medicine.
In a nutshell, we humans understand time by looking at a watch or a phone and thus we know what time it is. However, in the case of our body, it is a bit different. Every cell in our body has clock genes. As the name suggests, these genes are a clock that tells the cell what time it is, and the clock hand is… light! We have trillions of cells which contain such clocks. Consequently, you have trillions of clocks in your body that measure time with light.
These cells communicate with each other, creating in your body what we call the circadian rhythm which controls every biological process: from temperature regulation to hormone secretion, and your mood and energy levels.
The place that controls time in the human body is a certain region in the brain – the suprachiasmatic nucleus. This is where the synchronization of these trillion little clocks, necessary for the proper functioning of our body, takes place. This region in the brain is the “head” of all body biology, which gives commands to specific organs, tissues and cells.
A great example which illustrates how important the circadian rhythm is, is comparing it to an orchestra, comprising trillion cells in our body, where the conductor is light. If the musicians keep up with the conductor and there is synchronization in the whole orchestra, we hear wonderful music. Imagine a situation in which each orchestral instrument (cell phone) starts playing a different melody, that would lead to chaos and catastrophe. The effect of poor synchronization of the orchestra is unpleasant music, while disrupting the circadian rhythm will have inevitable health consequences, destroy our sleep and make it harder for us to stick to the diet.
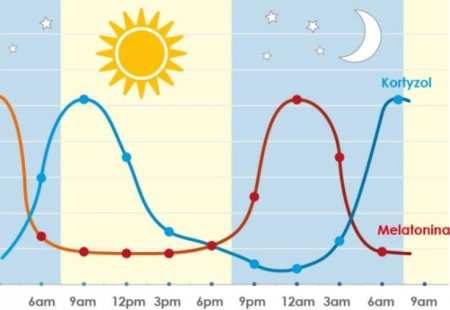
Here we come to melatonin, the sleep hormone that makes sure that we fall asleep, sleep well and regenerate at night. On the other hand, we have cortisol, the stress hormone that works in the opposite way to melatonin, that is, it stimulates us and makes us constantly awake.
Since melatonin calms us down and lulls us to sleep, its concentration should be highest after dark. On the other hand, cortisol is the opposite, its levels are high in the morning, when there’s natural sunlight, and then it should keep falling gently until dusk. That’s how it worked until Thomas Edison invented the light bulb. From then on, we’ve been able to lighten up our nights, which completely destroys the circadian rhythm and our biological clocks.
Light
Those first light bulbs didn’t have such a big impact on our circadian rhythm and sleep, but since 2012 LEDs have become widely used, including our computers, telephones, TVs, children’s toys, cars, public transport, streetlights, everywhere.
The human brain has not had the time to get used to the artificial blue light that is emitted by our electronic equipment, in front of which we spend most of our days.
It is the reason why our mind in the evening does not realize that it should calm down and prepare for sleep. This leads to impaired brain function and poor regeneration, which may have irreversible consequences in the long term. Below you can find a comparison of the natural light emitted by the sun to the LED light.
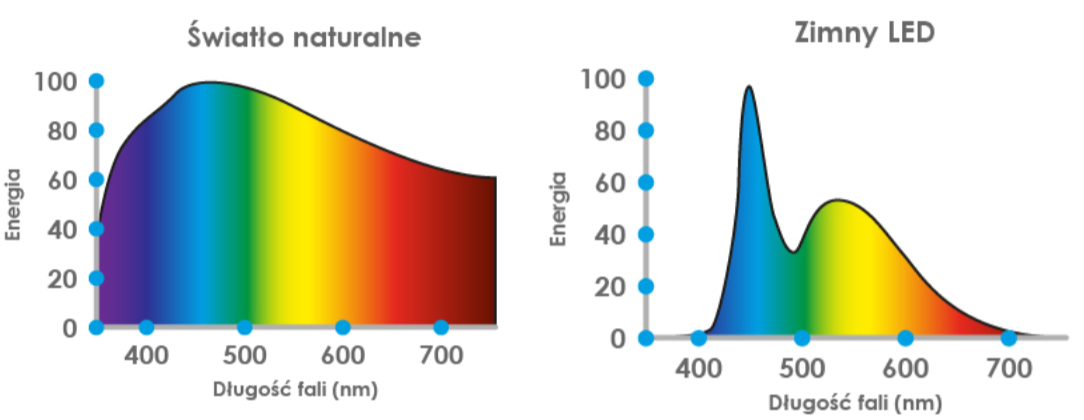
You can see that the light that LEDs emit is completely different than that of the sun, which our body has adapted to over millions of years of evolution.
It is also important that sunlight changes during the day, it’s a little different at 7am, at 10am, or 4pm, etc. Why is this happening? Because, as scientists have proven, light provides our body with information what time it is and what it should do at a given time. The activity of thyroid hormones will be highest at different times, we should feel most energized or feel like sleeping at different times.

On the other hand, the light emitted by our computer, telephone, TV or lighting at home / office is the same all the time and gives information to our body that it is noon. Currently, a vast majority of people live under the influence of artificial light 24 hours a day 7 days a week.
Light can be of different color, depending on the wavelength. All popular electronic devices, such as phones, laptops, TV, LED bulbs operate at wavelengths between 380 and 570 nm, i.e. the light they emit is blue, purple and green. And now, see the graph below, which shows which wavelengths destroy melatonin, our sleep and regeneration hormone, and compare it to the light provided by electronics, the LED lights.
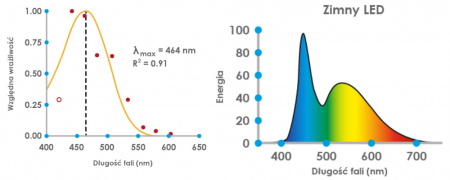
In the natural world it is dar when the sun goes down, there must be complete darkness at night. Looking at the phone/TV/laptop before going to sleep is not natural, let alone healthy, and is the main cause of sleep disturbance. Who doesn’t look at the phone/TV/laptop before going to sleep? I guess 99% of those who have made it so far do it. So let’s proceed.
Artificial light blocks the secretion of melatonin by up to 80% at the time when it should be dark. This means that if we watch TV before going to bed, look at the phone or laptop, or even read a book with the light on, we block our potential for better sleep and regeneration by 80%, causing the body to think that it is midday.
Ok, but is blue light harmful in itself? Or maybe there is a difference between natural blue light from the sun and that emitted by electronics?
It turns out there is a difference. In one of the graphs above, you can see that the light emitted by the sun has a so-called full spectrum. What does it mean? The point is that the sun emits each color of light in roughly equal proportion and has a lot of red and infrared in it. Our electronics, on the other hand, have a deficient light spectrum: a large amount of blue, a very small amount of red, virtually no infrared and UV light. This means that practically all day long we receive an unnaturally high amount of artificial blue light, and we lack the other colors.
What should we do to sleep better?
You already know that blue light is harmful and affects our sleep negatively. Now let’s move on to how to protect ourselves to sleep better and have more energy.
- Blue light filters for your computer / phone
There are certain apps we can run on our iPhone or Android or laptop that work in such a way that they reduce blue light. They are like a cigarette filter, they protect a little but not completely. We want 100% blue light blocking in the evening, and the filters are not up to the task.
You should also pay attention to the fact that the keyboard in the laptop or the lamp above your head is often on, and no filter can change it.
- Give up electronics 3-4 hours before bedtime
The most effective solution would be to put the electronics aside for 3-4 hours before bedtime and not to turn on the light, but let’s face it, in the 21st century it is unrealistic to say the least. On the other hand, it can be a very good habit to put down your electronics an hour before bedtime and read a book instead of watching series on Netflix.
- Anti-blue light glasses
What are those? Those are glasses with unusual lenses that have the ability to block blue light. They are the only effective protection, because by wearing them you cut off everything that goes directly to your eye. However, it’s a good idea to choose good quality blue light-blocking glasses as many of them don’t block the full spectrum of light effectively.
Bibliography:
- Irwin M i wsp. Partial sleep deprivation reduces natural killer cell activity in humans. Psychosom Med. 1994; 56(6):493-8.
- Cooper ChB i wsp. Sleep deprivation and obesity in adults: a brief narrative review. BMJ Journals.
- Daily Wellness. If You’re Sleeping Poorly, It Could Mean Your Estrogen Is Off. 2017
- Cheung IN. Morning and Evening Blue-Enriched Light Exposure Alters Metabolic Function in Normal Weight Adults. 2016
- Baron KG, Reid KJ. Circadian misalignment and health. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2014; 26(2):139-54.
- Lin HH, Farkas ME. Altered Circadian Rhythms and Breast Cancer: From the Human to the Molecular Level. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018; 9: 219.
- Savvidis Ch, Koutsilieris M. Circadian Rhythm Disruption in Cancer Biology. Mol Med. 2012; 18(1): 1249–1260.
- Theobald HE i wsp. Low-Dose Docosahexaenoic Acid Lowers Diastolic Blood Pressure in Middle-Aged Men and Women. The Journal of Nutrition, Volume 137, Issue 4, April 2007, Pages 973–978.








Comments No Comments
Join the discussion…