
Omega Fatty Acids – the Perfect Solution for Health?
You’ve probably come across the term omega fatty acids lots of times and you also might have heard about the recommendations to have at least two portions of fish a week, including oily sea fish. Why is it so important, what exactly are omega fatty acids, what are their properties and in what products can they be found? I’m going to answer all these questions today 🙂
Omega-3 and omega-6: the Essential Ingredients
Fatty acids that make up dietary fats can be divided according to various criteria, including: the type and number of double bonds in the molecule and the position of the first double bond. Omega fatty acids belong to the group of polyunsaturated fatty acids (they have more than one double bond in the molecule). The position of the first double bond determines their belonging to the family: omega-3, omega-6, omega-7, or omega-9.
The group of omega-3 and omega-6 acids are called essential fatty acids (EFA), which means that we must supply them with our diet because our body cannot produce them on its own.
The family of omega-3 fatty acids includes:
- α-linolenic acid (ALA),
- docosahexaenoic acid (DHA),
- eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA).
The omega-6 acids are:
- linoleic acid (LA),
- arachidonic acid (ARA).
The Perfect Solution for Good Health – the Properties
Fats are an important component of the diet, which I wrote more about HERE. In this entry, I would like to draw your attention to omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which have numerous beneficial properties. They are necessary for:
- proper maturation and development of the nervous system;
- proper functioning of the visual organ;
- optimal functioning of the immune system.
What’s more, the recommended intake of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids balances lipid metabolism (contributes to maintaining appropriate HDL and LDL cholesterol levels), improves the functioning of the cardiovascular system, and prevents inflammation.
Research studies have shown that omega-3 fatty acids are an important support in the therapy and treatment of obesity, intestinal microbiota disorders, metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, neurodegenerative diseases (dementia, Alzheimer’s disease) and depression.
As you can see, the action of omega acids is multidirectional and supports the functioning of the body in almost every area.
How Much and Where From?
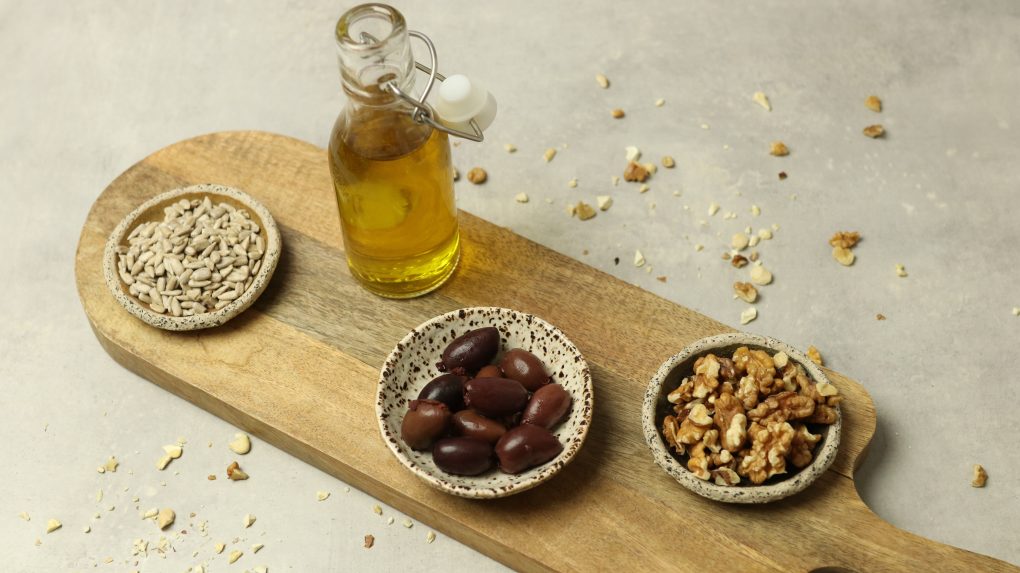
The sources of omega-6 fatty acids and their precursors are mainly: safflower oil, sunflower oil, evening primrose oil, nuts, seeds, as well as meat and eggs. Omega-3 fatty acids are mainly present in oily sea fish (salmon, herring, mackerel, rainbow trout, tuna, sardine), seafood, algae, as well as walnuts, linseed, linseed oil, soybean oil and rapeseed oil.
It is recommended for healthy people to eat fish regularly, at least twice a week, including oily sea fish. This should cover the need for omega-3 fatty acids DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) and EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), which is 250 mg per day. The recommended share of ALA (α-linolenic acid) is expressed as a percentage – 0.5% of the total energy intake per day, and for LA (linoleic acid) – 4%.
You may be concerned about fish contamination with heavy metals. If possible, you can check what region the purchased fish comes from and the degree of pollution of the waters, or limit the consumption of predatory fish species (swordfish, shark, king mackerel, tuna) that are potentially the most polluted. It is worth paying attention to this fact, especially in the case of pregnant women, lactating women and children, but remember that this does not mean you should completely cut out fish from the diet.
I also want to emphasize that pregnant and breastfeeding women should supplement omega-3 DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), which is necessary for the proper course of pregnancy and child development (at least 200 mg of DHA per day). Sometimes it is worth considering supplementation also in the preconception period or higher doses of the supplement should be used (when there is a risk of premature birth), which should be agreed with the doctor supervising the pregnancy.
Omega-3 fatty acids are very important in the diet of infants, children and adolescents, which is related to their significant development and functioning of the nervous system. Children and adolescents should also eat fish (including oily sea fish) or supplement DHA and EPA acids.
Supplementation – Yes or No?
If you do not eat fish (e.g. due to a vegetarian or vegan diet), the decision to supplement with omega-3 acids may be necessary. Fortunately, there are various algae-based preparations available on the market. I know that in Poland not everyone has the opportunity to eat fish and seafood regularly due to their poor availability and relatively high price. If you only eat fish occasionally, it is also worth considering supplementation and choosing a product based on fish oils (Levann’s offer includes, among others, Omega-3 + D3 + K2 + E HERE).
When choosing a supplement, pay attention to the amount of fatty acids declared by the manufacturer on the packaging, as well as the presence of antioxidants (e.g. vitamin E).
Also remember not to store the preparation at high temperatures or expose it to sunlight, as this promotes the oxidation of fats, as a result of which the supplement will not fulfill its function.
Summary
Omega fatty acids are an essential component of the diet, so make sure your menu includes fish, nuts, seeds, and healthy oils. If you lack culinary inspiration, visit my blog and the Diet & Training by Ann application (HERE), where you will find plenty of healthy recipes.
Remember not to be afraid of fats, because as you can see, we really do need them!🙂
Bibliography:
- Djuricic I, Calder PC. Beneficial Outcomes of Omega-6 and Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Human Health: An Update for 2021. Nutrients. 2021; 13(7):2421
- Narodowy Instytut Zdrowia Publicznego – PZH. Normy żywienia dla populacji Polski i ich zastosowanie. 2020
- Sicińska P, Pytel E, Kurowska J, Koter-Michalak M. Suplementacja kwasami omega w różnych chorobach. Postepy Hig Med Dosw. 2015; 69: 838-852
- Zimmer M, Sieroszewski P, Oszukowski P, Huras H, Fuchs T, Pawłosek A. Rekomendacje Polskiego Towarzystwa Ginekologów i Położników dotyczące suplementacji u kobiet ciężarnych. Ginekologia i Perinatologia Praktyczna. 2020; 5(4):17-181








Comments No Comments
Join the discussion…